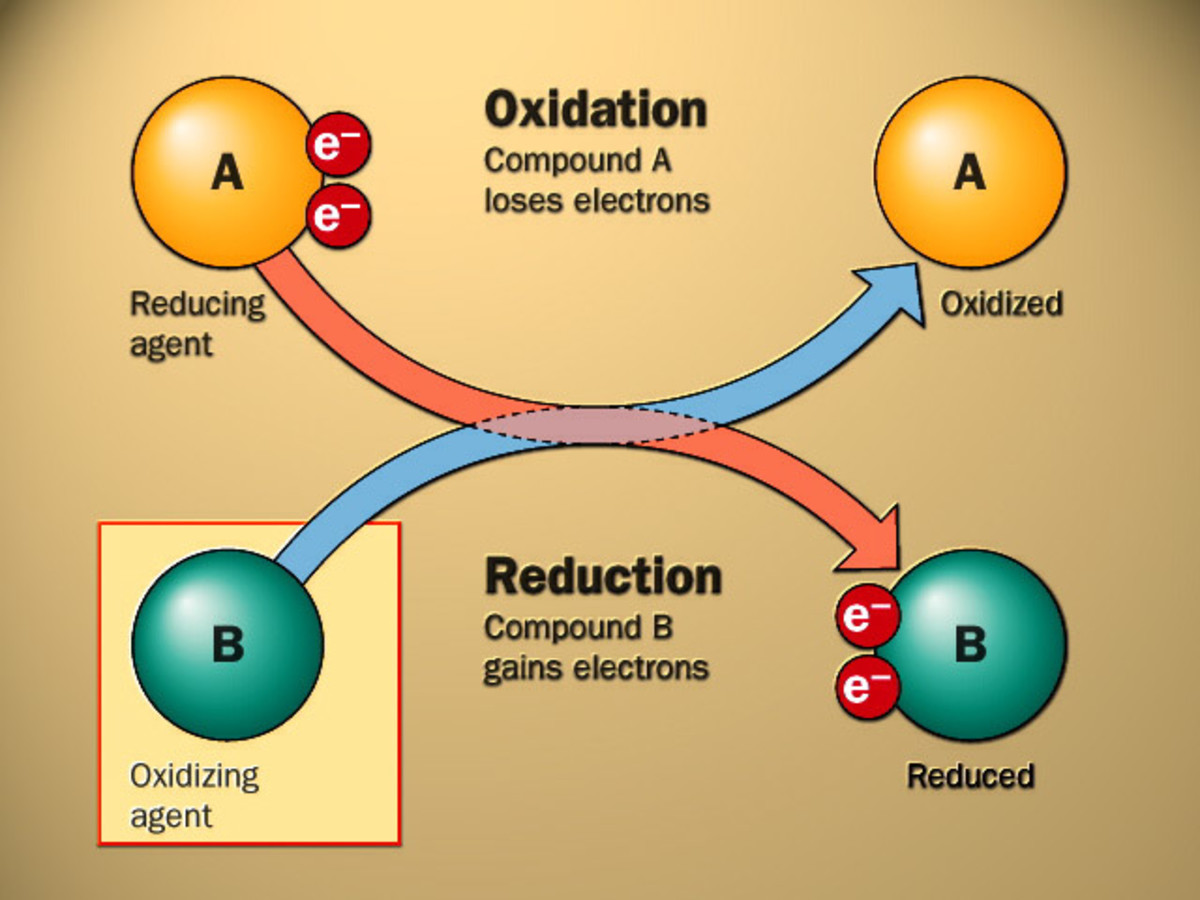
BasicsRedox (reduction-oxidation, pronunciation: /ˈrɛdɒks/ RED-oks or /ˈriːdɒks/ REE-doks) is a sort of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of atoms are modified. Redox reactions are characterized with the aid of manner of the actual or formal transfer of electrons among chemical species, most often with one species (the reducing agent) undergoing oxidation (losing electrons) whilst some other species (the oxidizing agent) undergoes discount (gains electrons). The chemical species from which the electron is eliminated is stated to have been oxidized, at the same time as the chemical species to which the electron is brought is said to have been decreased. In different words:
Oxidation is the lack of electrons or a boom inside the oxidation kingdom of an atom, an ion, or of sure atoms in a molecule.
Reduction is the advantage of electrons or a lower inside the oxidation kingdom of an atom, an ion, or of sure atoms in a molecule (a reduction in oxidation state).
Many reactions in organic chemistry are redox reactions due to modifications in oxidation states however without first-rate electron transfer. For instance, in some unspecified time in the future of the combustion of timber with molecular oxygen, the oxidation of an of carbon atoms inside the wooden increases, and that of oxygen atoms decreases as carbon dioxide and water are shaped. The oxygen atoms go through cut-price, formally gaining electrons, whilst the carbon atoms undergo oxidation, dropping electrons. Thus oxygen is the oxidizing agent and carbon is the decreasing agent in this response.
Although oxidation reactions are usually related to the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, oxygen is not continually covered in such reactions, as exceptional chemical species can serve the same characteristic.
Redox reactions can occur quite slowly, as inside the formation of rust, or masses extra rapidly, as inside the case of burning gas. There are easy redox approaches, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the discount of carbon through hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and further complex methods along with the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) inside the human frame. Analysis of bond energies and ionization energies in water allows calculation of the redox potentials.
Etymology
"Redox" is a portmanteau of the phrases "discount" and "oxidation". The phrase oxidation, in the beginning, implied reaction with oxygen to shape an oxide, due to the truth dioxygen (O2(g)) modified into traditionally the primary recognized oxidizing agent. Later, the term modified expanded to embody oxygen-like substances that finished parallel chemical reactions. Ultimately, this means that becomes generalized to embody all procedures concerning the loss of electrons.
The phrase reduction at the beginning referred to the loss in weight upon heating a metal ore along with a steel oxide to extract the metallic. In exclusive terms, ore becomes "reduced" to metal. Antoine Lavoisier established that this loss of weight was because of the dearth of oxygen as a gas. Later, scientists found out that the metallic atom profits electrons on this system. This means that reduction then has become generalized to encompass all techniques concerning the advantage of electrons.
The electrochemist John Bockris has used the terms electronation and deelectronation to give an explanation for reduction and oxidation techniques, respectively, when they arise at electrodes. These phrases are analogous to protonation and deprotonation,[8] but they have got not been widely adopted by using chemists worldwide.
The time period "hydrogenation" might also need to regularly be used in preference to cut price, due to the fact hydrogen is the lowering agent in a big range of reactions, especially in organic chemistry and biochemistry. However, not like oxidation, which has been generalized past its root element, hydrogenation has maintained its precise connection to reactions that add hydrogen to each other substance (e.G., the hydrogenation of unsaturated fat into saturated fats, R−CH=CH−R + H2 → R−CH2−CH2−R). The word "redox" modified into first utilized in 1928.
Definitions
The methods of oxidation and bargain arise concurrently and cannot display up independently of every other, just like acid-base reactions. The oxidation by myself and the bargain by myself are each referred to as a half-response because of the reality half of-reactions always arise collectively to shape a whole response. When writing 1/2 of-reactions, the acquired or misplaced electrons are usually covered explicitly simply so the half-reaction is balanced with admire to electric charge. The electrons cancel out whilst the 1/2 of-reactions are mixed to make the internet chemical equation.[citation needed]
Though sufficient for plenty of functions, those widespread descriptions aren't precisely accurate. Although oxidation and bargain properly talk with an exchange in the oxidation kingdom, the real switch of electrons can also never arise. The oxidation kingdom of an atom is the fictional price that an atom may want to have if all bonds among atoms of various factors were one hundred% ionic. Thus, oxidation is greatly defined as an increase in oxidation us of a, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation u . S . A. In exercise, the switch of electrons will usually purpose a trade in the oxidation kingdom, but numerous reactions can be classed as "redox" even though no electron switch takes vicinity (including the ones concerning covalent bonds). As an end result, simple half of the of-reactions cannot be written for the character atoms present process a redox method.[citation needed]
Oxidizing and decreasing marketers
In redox strategies, the reductant transfers electrons to the oxidant. Thus, in the reaction, the reductant or decreasing agent loses electrons and is oxidized, and the oxidant or oxidizing agent profits electrons and is decreased. The pair of oxidizing and degreasing agents that are involved in a specific reaction is called a redox pair. A redox couple is a reducing species and its corresponding oxidizing shape, e.G., Fe2+
/ Fe3+
.
Oxidizers
Substances that have the capability to oxidize other substances (cause them to lose electrons) are stated to be oxidative or oxidizing and are known as oxidizing agents, oxidants, or oxidizers. That is, the oxidant (oxidizing agent) receives rid of electrons from some other substance, and is because of this itself decreased. And, because it "accepts" electrons, the oxidizing agent is also called an electron acceptor. Oxygen is the critical oxidizer.
Oxidants are generally chemical materials with factors in high oxidation states (e.G., H
2O
2, MnO−
4, CEO
three, Cr
2O2−
7, OsO
four), otherwise enormously electronegative factors (O2, F2, Cl2, Br2) that may advantage greater electrons with the aid of the usage of oxidizing some other substance.[citation needed]
Reducers
Substances that have the capacity to reduce other materials (motive them to benefit electrons) are said to be reductive or decreasing and are called lowering retailers, reductants, or reducers. The reductant (decreasing agent) transfers electrons to every different substance and is accordingly oxidized. And, because it donates electrons, the lowering agent is likewise referred to as an electron donor. Electron donors also can shape rate switch complexes with electron acceptors.
Reductants in chemistry are very various. Electropositive elemental metals, such as lithium, sodium, magnesium, iron, zinc, and aluminum, are appropriate reducing sellers. These metals donate or supply away electrons noticeably pretty absolutely. Hydride transfer reagents, collectively with NaBH4 and LiAlH4, are broadly applied in herbal chemistry, inside the primary in the cut price of carbonyl compounds to alcohols. Another approach of discount entails the use of hydrogen gasoline (H2) with palladium, platinum, or nickel catalyst. The catalytic hydrogenation response is a critical business method.
Standard electrode potentials (discount potentials)
Each 1/2 of-response has a standard electrode capability (E0
cell), that's identical to the capability difference or voltage at equilibrium underneath preferred conditions of an electrochemical cellular wherein the cathode response is the half of-response taken into consideration, and the anode is an ultra-modern hydrogen electrode where hydrogen is oxidized:
1⁄2 H2 → H+ + e−.
The electrode capability of each half of-response is likewise referred to as its discount ability E0
crimson, or capability at the same time as the half-reaction takes area at a cathode. The reduction capacity is the degree of the tendency of the oxidizing agent to be decreased. Its value is 0 for H+ + e− → 1⁄2 H2 thru definition, powerful for oxidizing sellers more potent than H+ (e.G., +2.866 V for F2) and awful for oxidizing dealers which can be weaker than H+ (e.G., −zero.763 V for Zn2+).
For a redox reaction that takes vicinity in a mobile, the potential distinction is:
E0
cell = E0
cathode – E0
anode
However, the capacity of the response at the anode is now and again expressed as an oxidation potential:
E0
ox = –E0
crimson.
The oxidation capability is a degree of the tendency of the decreasing agent to be oxidized however does not represent the physical functionality at an electrode. With this notation, the mobile voltage equation is written with a plus sign
E0
mobile = E0
pink(cathode) + E0
ox(anode)
Examples of redox reactions
Illustration of a redox response
In the reaction between hydrogen and fluorine, hydrogen is being oxidized and fluorine is being reduced:
H
2 + F
2 → 2 HF
This reaction is spontaneous and releases 542 kJ consistent with 2 g of hydrogen because of the reality the H-F bond is a superb deal stronger than the vulnerable, high-energy F-F bond. We can write this common response as half-reactions:
the oxidation reaction:
H
2 → 2 H+ + 2 e−
and the reduction reaction:
F
2 + 2 e− → 2 F−
Analyzing each 1/2-response in isolation can often make the overall chemical technique clearer. Because there may be no net change in charge in the route of a redox reaction, the range of electrons in extra in the oxidation response has to identify the variety ate up through the discount response (as shown above).
Elements, even in molecular shape, usually have an oxidation nation of 0. In the first half of the reaction, hydrogen is oxidized from an oxidation state of 0 to an oxidation country of +1. In the second half of the reaction, fluorine is decreased from an oxidation u . S . A. Of zero to an oxidation kingdom of −1.
When which include the reactions together the electrons are canceled:
H
2 → 2 H+ + 2 e−
F
2 + 2 e− → 2 F−
H2 + F2 → 2 H+ + 2 F−
And the ions integrate to shape hydrogen fluoride:
2 H+ + 2 F− → 2 HF
The ordinary response is:
H
2 + F
2 → 2 HF
Metal displacement
A redox response is a pressure in the again of an electrochemical cellular like the Galvanic mobile pictured. The battery is made from a zinc electrode in a ZnSO4 solution associated with a cord and a porous disk to a copper electrode in a CuSO4 solution.
In this type of reaction, a metal atom in a compound (or in an answer) is changed through an atom of every other steel. For instance, copper is deposited whilst zinc steel is placed in a copper(II) sulfate solution:
Zn(s)+ CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
In the above response, zinc metal displaces the copper(II) ion from copper sulfate solution and consequently liberates free copper metallic. The reaction is spontaneous and releases 213 kJ consistent with 65 g of zinc due to the fact relative to zinc, copper steel is lower in energy due to bonding via its in part stuffed d-orbitals.
The ionic equation for this reaction is:
Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu
As 1/2 of-reactions, it's miles visible that the zinc is oxidized:
Zn → Zn2+ + 2 e−
And the copper is reduced:
Cu2+ + 2 e− → Cu
Other examples
The reduction of nitrate to nitrogen in the presence of an acid (denitrification):
2 NO−
three + 10 e− + 12 H+ → N2 + 6 H2O
The combustion of hydrocarbons, which include in an inner combustion engine, produces water, carbon dioxide, a few partially oxidized forms together with carbon monoxide, and heat electricity. Complete oxidation of substances containing carbon produces carbon dioxide.
In natural chemistry, the stepwise oxidation of a hydrocarbon using oxygen produces water and, successively, alcohol, an aldehyde or a ketone, a carboxylic acid, and then a peroxide.
Corrosion and rusting
Oxides, in conjunction with iron(III) oxide or rust, which includes hydrated iron(III) oxides Fe2O3·nH2O and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH), Fe(OH)3), shape at the same time as oxygen combines with extraordinary factors
Iron rusting in pyrite cubes
The term corrosion refers to the electrochemical oxidation of metals in response to an oxidant which includes oxygen. Rusting, the formation of iron oxides is a famous example of electrochemical corrosion; it paperwork due to the oxidation of iron metallic. Common rust regularly refers to iron(III) oxide, customary in the following chemical response:
4 Fe + 3 O2 → 2 Fe2O3
The oxidation of iron(II) to iron(III) by using the usage of hydrogen peroxide within the presence of an acid:
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e−
H2O2 + 2 e− → 2 OH−
Overall equation:
2 Fe2+ + H2O2 + 2 H+ → 2 Fe3+ + 2 H2O
Disproportionation
A disproportionation response is one in which a single substance is each oxidized and reduced. For instance, thiosulfate ion with sulfur in oxidation state +2 can react within the presence of acid to form elemental sulfur (oxidation country zero) and sulfur dioxide (oxidation country +4).
S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) → S(s) + SO2(g) + H2O(l)
Thus one sulfur atom is reduced from +2 to 0, even as the opposite is oxidized from +2 to +4.[14]
Redox reactions in enterprise
Cathodic protection is a technique used to control the corrosion of a metal ground by using making it the cathode of an electrochemical mobile. A simple approach of safety connects blanketed steel to an extra without problems corroded "sacrificial anode" to act because of the anode. The sacrificial metallic instead of the protected metal, then, corrodes. A common software program of cathodic safety is in galvanized metallic, in which a sacrificial coating of zinc on steel components protects them from rust.[citation needed]
Oxidation is used in a huge shape of industries which includes inside the production of cleaning products and oxidizing ammonia to provide nitric acid.
Redox reactions are the muse of electrochemical cells, that can generate electrical strength or assist electrosynthesis. Metal ores regularly incorporate metals in oxidized states which incorporates oxides or sulfides, from which the natural metals are extracted through smelting at the high temperature inside the presence of a decreasing agent. The gadget of electroplating uses redox reactions to coat objects with a skinny layer of a material, as in chrome-plated car additives, silver plating cutlery, galvanization, and gold-plated rings.[citation needed]
Redox reactions in biology
ascorbic acid
dehydroascorbic acid
Top: ascorbic acid (a decreased form of Vitamin C)
Bottom: dehydroascorbic acid (oxidized form of Vitamin C)
Enzymatic browning is an instance of a redox response that takes vicinity in maximum fruits and vegetables.
Many important natural techniques contain redox reactions. Before a number of those techniques can start iron must be assimilated from the surroundings.
Cellular respiratory, as an instance, is the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) to CO2 and the discount of oxygen to water. The summary equation for mobile respiratory is:
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
The device of cellular respiratory also depends heavily on the discount of NAD+ to NADH and the opposite response (the oxidation of NADH to NAD+). Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are complementary, however, photosynthesis isn't the alternative to the redox response in cellular respiratory:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + moderate electricity → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Biological electricity is regularly stored and released with the useful resource of redox reactions. Photosynthesis entails the reduction of carbon dioxide into sugars and the oxidation of water into molecular oxygen. The opposite response, respiratory, oxidizes sugars to provide carbon dioxide and water. As intermediate steps, the reduced carbon compounds are used to lessen nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to NADH, which then contributes to the advent of a proton gradient, which drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and is maintained through the discount of oxygen. In animal cells, mitochondria carry out similar capabilities. See the Membrane capability article.
Free radical reactions are redox reactions that occur as part of homeostasis and killing microorganisms, wherein an electron detaches from a molecule after which reattaches almost immediately. Free radicals are part of redox molecules and can come to be risky to the human body inside the occasion that they do now not reattach to the redox molecule or an antioxidant. Unsatisfied free radicals can spur the mutation of cells they come across and are, because of this, motives of most cancers.
The time period redox state is regularly used to explain the stability of GSH/GSSG, NAD+/NADH, and NADP+/NADPH in an organic gadget together with a cell or organ. The redox country is pondered inside the balance of several units of metabolites (e.G., lactate and pyruvate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate), whose interconversion is dependent on the one's ratios. An abnormal redox nation can increase in quite a few deleterious situations, together with hypoxia, surprise, and sepsis. Redox mechanism additionally manages some mobile techniques. Redox proteins and their genes ought to be co-located for redox law consistent with the CoRR hypothesis for the characteristic of DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Redox biking
Wide sorts of fragrant compounds are enzymatically reduced to shape unfastened radicals that incorporate one more electron than their determined compounds. In desired, the electron donor is any of a big sort of flavoenzymes and their coenzymes. Once shaped, the one's anion free radicals reduce molecular oxygen to superoxide and regenerate the unchanged determined compound. The internet response is the oxidation of the flavoenzyme's coenzymes and the bargain of molecular oxygen to shape superoxide. This catalytic conduct has been defined as a futile cycle or redox biking.
Redox reactions in geology
Mi Vida uranium mine, close to Moab, Utah. The alternating red and white/inexperienced bands of sandstone correspond to oxidized and decreased situations in groundwater redox chemistry.
In geology, redox is crucial to both the formation of minerals and the mobilization of minerals and is also critical in some depositional environments. In preferred, the redox kingdom of most rocks can be seen within the color of the rock. The rock paperwork in oxidizing situations, giving it a red shade. It is then "bleached" to a green—or sometimes white—form even as a decreasing fluid passes through the rock. The reduced fluid can also convey uranium-bearing minerals. Famous examples of redox conditions affecting geological strategies include uranium deposits and Moqui marbles.[citation needed]
Redox reactions in soils
Electron transfer reactions are important to myriad techniques and homes in soils, and electron "hobby", quantified as Eh (platinum electrode capacity (voltage) relative to the same old hydrogen electrode) or pe (analogous to pH as -log electron hobby, is a grasp variable, along with aspect pH, that controls and is ruled by using chemical reactions and biological processes. Early theoretical studies with packages to flooded soils and paddy rice production were seminal for subsequent artwork on thermodynamic factors of redox and plant root increase in soils. Later artwork built in this foundation, and improved it for understanding redox reactions related to heavy metal oxidation u . S . Modifications, pedogenesis and morphology, natural compound degradation and formation, unfastened radical chemistry, wetland delineation, soil remediation, and diverse methodological processes for characterizing the redox reputation of soils.
Balancing redox reactions
Describing the general electrochemical reaction for a redox way requires balancing the element half-reactions for oxidation and reduction. In fashionable, for reactions in aqueous solution, this involves which includes H+, OH−, H2O, and electrons to compensate for the oxidation changes.
Acidic media
In acidic aqueous media, H+ ions and water are introduced to half of-reactions to stability the overall response.
For instance, while manganese(II) reacts with sodium bismuthate:
Unbalanced response: Mn2+(aq) + NaBiO3(s) → Bi3+(aq) + MnO−
4 (aq)
Oxidation: 4 H2O(l) + Mn2+(aq) → MnO−
four(aq) + 8 H+(aq) + 5 e−
Reduction: 2 e− + 6 H+ + BiO−
three(s) → Bi3+(aq) + three H2O(l)
The reaction is balanced thru scaling the two 1/2-cell reactions to contain the equal range of electrons (multiplying the oxidation reaction by way of manner of the range of electrons in the cut price step and vice versa):
eight H2O(l) + 2 Mn2+(aq) → 2 MnO−
four(aq) + sixteen H+(aq) + 10 e−
10 e− + 30 H+ + 5 BiO−
3(s) → 5 Bi3+(aq) + 15 H2O(l)
Adding those reactions removes the electrons terms and yields the balanced response:
14 H+(aq) + 2 Mn2+(aq) + five NaBiO3(s) → 7 H2O(l) + 2 MnO−
four(aq) + 5 Bi3+(aq) + five Na+
(aq)
Basic media
In simple aqueous media, OH− ions and water are added to half of-reactions to stability the overall response.
For instance, inside the response among potassium permanganate and sodium sulfite:
Unbalanced reaction: KMnO4 + Na2SO3 + H2O → MnO2 + Na2SO4 + KOH
Reduction: 3 e− + 2 H2O + MnO−
four → MnO2 + four OH−
Oxidation: 2 OH− + SO2−
three → SO2−
4 + H2O + 2 e−
Balancing the number of electrons inside the two 1/2 of-cellular reactions gives:
6 e− + four H2O + 2 MnO−
four → 2 MnO2 + eight OH−
6 OH− + three SO2−
three → SO2−
four + 3 H2O + 6 e−
Adding the ones half of-cell reactions together gives the balanced equation:
2 KMnO4 + 3 Na2SO3 + H2O → 2 MnO2 + 3 Na2SO4 + 2 KOH
Mnemonics
Main article: List of chemistry mnemonics
The key terms involved in redox are regularly difficult. For example, a reagent that is oxidized loses electrons; however, that reagent is referred to as the reducing agent. Likewise, a reagent that is reduced gains electrons and is called the oxidizing agent. These mnemonics are usually used by college students to help memorize the terminology:
"OIL RIG" — oxidation is loss of electrons, a discount is an advantage of electrons
"LEO the lion says GER [grr]" — lack of electrons is oxidation, an advantage of electrons is discount
"LEORA says GEROA" — the dearth of electrons is known as oxidation (reducing agent); the gain of electrons is called reduction (oxidizing agent).
"RED CAT" and "AN OX", or "AnOx RedCat" ("an ox-purple cat") — cut-price takes place on the cathode and the anode is for oxidation
"RED CAT profits what AN OX loses" – bargain on the cathode profits (electrons) what anode oxidation loses (electrons)
"PANIC" – Positive Anode and Negative is Cathode. This applies to electrolytic cells which launch stored power and maybe recharged with energy. PANIC does now not practice to cells that can be recharged with redox materials. These galvanic or voltaic cells, in conjunction with gasoline cells, produce power from inner redox reactions. Here, the powerful electrode is the cathode and the horrible is the anode.




![Is Helium a Noble Gas? [ EDU Science ]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhnf4spv6HGlGiVe5Zu3zN6z4KP91ZQfpPrQurkHaeBksi6eOYDbVr1Cyvfd51AP99ebC48IwK2xsGZIarbflINNfC5_FFYrfqg3h1qNR01uUzM_umyNUg2S5c8aWHKQLjBYSE9UoHSIw/w100/cartoon-happy-frog_160606-288-removebg-preview+%25283%2529.png)
![What is aerodynamics?[ EDU Science ]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhN4R6-c-aaMLVew58tuGqq54Gu1bN6I1ICP_wLrCZPVI9UttDlBVIMNzn9OGrIlSJ8sGwgb5JBsH8E8eMxy-sjgUmOIZvBjcE8OWuPMOauTQdjFe1slakhBWpqfeqZB8HHnLouFN_uNg/w100/unnamed.jpg)
0 Comments
If you have any doubt let me know.